Supply and Demand: Crash Course Economics #4
null
Click
Use
to move to a smaller summary and to move to a larger one
The Efficiency and Benefits of Markets
- Markets are places where buyers and sellers meet to exchange goods and services.
- Voluntary exchange is the key concept of markets, where both parties willingly decide to make a transaction.
- Markets exist in various forms, such as farmer's markets and labor markets.
- Competitive markets efficiently allocate scarce resources towards their most efficient use.
- Price signals generated by markets guide the distribution of resources.
- Markets incentivize the production of high-quality products.
- Businesses in transparent markets have a hard time taking advantage of consumers.
- Consumer choice plays a significant role in the functioning of markets.
Understanding Supply and Demand in Economics
- Prices and profit determine the allocation of resources.
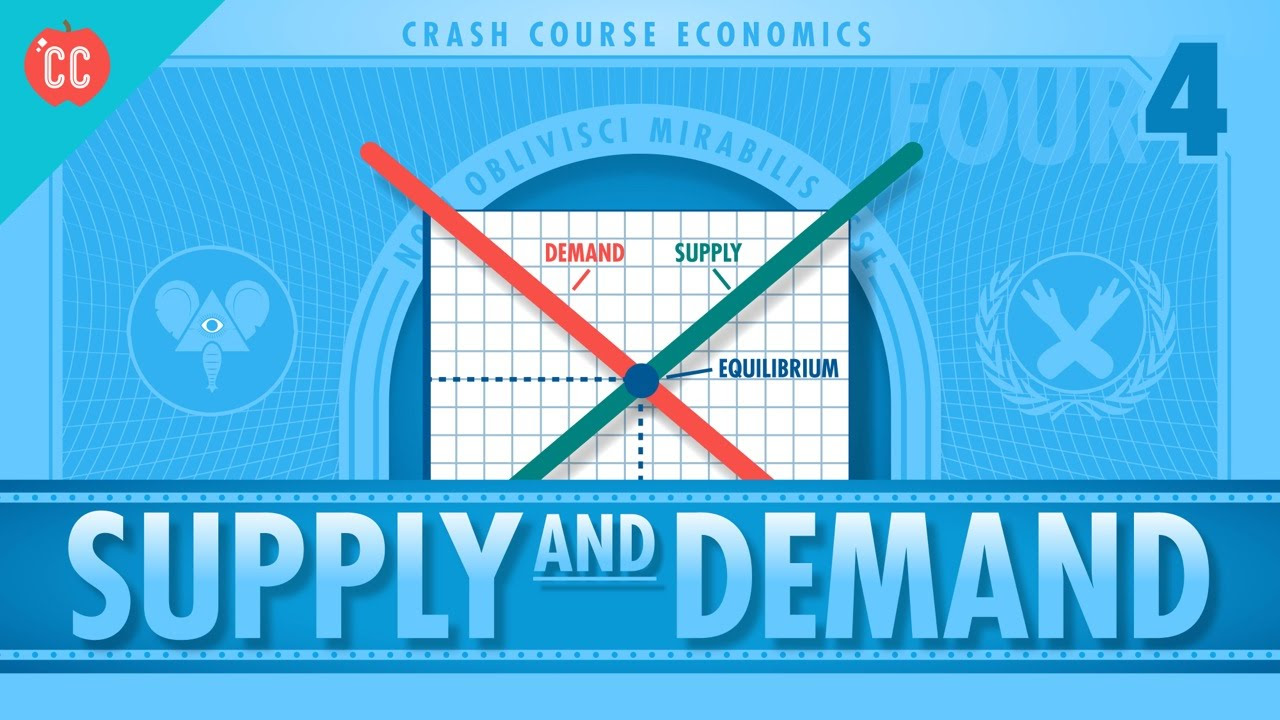
- Supply and demand determine prices in a market.
- The law of demand states that as prices increase, buyers purchase less, and as prices decrease, buyers purchase more.
- The law of supply states that as prices increase, sellers have an incentive to produce more, and as prices decrease, sellers have less incentive to produce.
- The intersection of supply and demand determines the equilibrium price and quantity.
- External factors such as weather can shift the supply curve.
- Changes in supply and demand can affect the equilibrium price and quantity.
- There are four possible outcomes in a market: decrease in supply, increase in supply, decrease in demand, or increase in demand.
- The perception of a fair or right price is subjective and varies between buyers and sellers.
- Economists believe that prices are determined by voluntary exchange and serve a purpose in the market.
The Limitations and Ethical Considerations of Market Approaches
- The demand curve for strawberries shifts to the left, causing a decrease in equilibrium price and quantity.
- Government bailouts for farmers may not be necessary as the market has spoken.
- Subsidizing farmers would allocate resources towards something society does not value, resulting in inefficiency.
- The supply and demand model applies to various markets, including gasoline.
- Fluctuating gas prices in 2014 were a result of weakened demand and increased supply.
- Markets and supply and demand are generally beneficial, but there are exceptions.
- Using a market approach for essential services like firefighting is not appropriate.
- The question of whether there should be a market for human organs raises ethical concerns.
- An unregulated market for human kidneys raises moral questions and incentivizes illegal activities.
- Regulated markets, such as kidney exchanges, can help increase the supply of donated organs and address shortages.
The Role of Supply and Demand in Economics
- Supply and demand are key concepts in economics.
- They are not absolute laws like the law of gravity, but rather behaviors influenced by human choices.
- Human actions as buyers and sellers directly impact supply and demand.
- Economic laws should be understood in the context of human decision-making.
Understanding Markets and the Role of Supply and Demand
- Markets are where buyers and sellers meet to exchange goods and services.
- Voluntary exchange is the foundation of markets, with both parties willingly participating in transactions.
- Different types of markets exist, such as farmer's markets and labor markets.
- Competitive markets efficiently allocate limited resources to their most efficient use.
- Price signals in markets guide resource distribution and incentivize the production of high-quality products.
- Transparent markets make it difficult for businesses to take advantage of consumers.
- Consumer choice plays a significant role in market functioning.
- Prices and profit determine resource allocation in markets.
- Supply and demand determine prices in markets.
- The law of demand states that as prices increase, buyers purchase less, and vice versa.
- The law of supply states that as prices increase, sellers produce more, and vice versa.